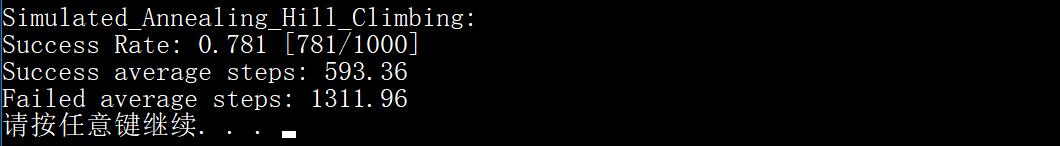使用爬山法、模拟退火和遗传算法求解八皇后问题
实验使用 C++ 语言,并在 Windows 的 Visual Studio 2017 下能够正常运行。
参考书籍:《人工智能:一种现代的方法(第三版)》
1. 准备阶段 1.1 Board 类
Board 类数据成员
bool board[8][8]:表示一个 8$\times$8 棋盘的具体情况。某位值为 true 时(即 1),表示该位上为皇后,否则为 false(即 0),表示该位上没有放置任何东西。
int state[8]:表示当前棋盘的状态。使用一个 8 位数串来表示八皇后问题的一个特定的状态。比如 83742516 就表示了这样的一个状态(注意加粗部分):
第 1 列第 8 行位置有一个皇后
第 2 列第 3 行位置有一个皇后
第 3 列第 7 行位置有一个皇后
…
第 8 列第 6 行位置有一个皇后
int h_value_board[8][8]:一个辅助数据成员,表示一个 8$\times$8 棋盘上的所有下一步状态的评估值 —— 相互攻击的皇后的对数。其对应于书本上的下图:
方格中显示的数字表示将这一列中的皇后移到该方格而得到的后继状态的评估值。
Board 类函数成员
void initial():将棋盘 board 初始化,初始化后棋盘上不会放置任何皇后。void fill_in_board():内部先调用了一次 initial(),然后根据 state 数据成员往棋盘 board 放入 8 个皇后。void random_initial_state():随机产生一个初始状态,赋值给 state 数据成员。void display(int mode):打印当前棋盘的信息,mode 参数用于选择打印方式。void display_h_value_on_board():打印当前棋盘的 h_value_board 数据成员。void set_state(string state_):手动设置初始状态 state 而不是随机产生。string get_state():获得 state 数据成员bool check(int mode): 检查当前棋盘上八皇后的放置是否已经满足要求,也即八皇后问题是否成功求解。mode 参数用于选择检查方式。int h_of_attack_pair():启发式评估函数 —— 相互攻击的皇后的数量。int h_of_not_attack_pair():启发式评估函数 —— 不相互攻击的皇后的数量。int count_attack(int x, int y):给定皇后的位置 x 和 y,该函数计算在棋盘 (x, y) 位置上的皇后与多少个其他位置上的皇后形成相互攻击 。
1.2 其他全局变量 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 int SHC_success_total_steps = 0 ; int SHC_failed_total_steps = 0 ; int FCHC_success_total_steps = 0 ; int FCHC_failed_total_steps = 0 ; int RRSHC_success_total_steps = 0 ; int RRSHC_failed_total_steps = 0 ; int SA_success_total_steps = 0 ; int SA_failed_total_steps = 0 ; int generation = 0 ; Board b_tool;
2. 爬山法
具体实现了最陡上升爬山法,首选爬山法和随机重启爬山法。
2.1 最陡上升爬山法 2.1.1 代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 bool Steepest_Hill_Climbing (Board* board) int steps = 0 ; string old_state = board->get_state (); string new_state = old_state; string best_state = old_state; int min_h = board->h_of_attack_pair (); int new_h; while (1 ) { ++steps; bool local_max_flag = true ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 8 ; ++j) { if (old_state[i] != j + '0' ) { new_state = old_state; new_state[i] = j + '0' ; board->set_state (new_state); board->fill_in_board (); new_h = board->h_of_attack_pair (); board->h_value_board[j][i] = new_h; if (new_h < min_h) { min_h = new_h; best_state = new_state; local_max_flag = false ; if (min_h == 0 ) { SHC_success_total_steps += steps; return true ; } } } else board->h_value_board[j][i] = 0 ; } } board->set_state (best_state); board->fill_in_board (); old_state = best_state; if (local_max_flag) { SHC_failed_total_steps += steps; return false ; } } }
2.1.2 测试
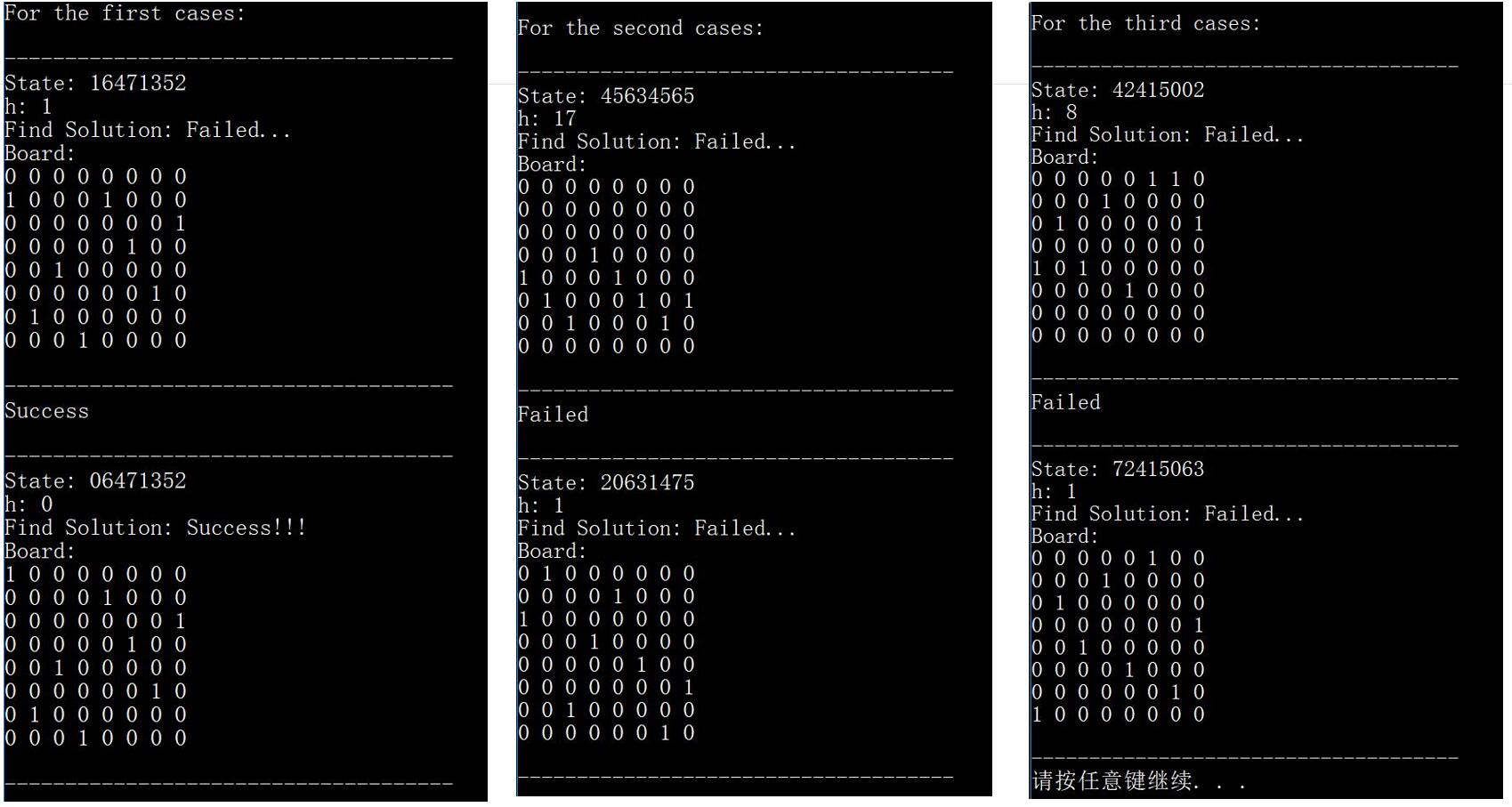
void SHC_test1():最陡上升爬山法测试函数 —— 进行 3 次最陡上升爬山法求解测试,分别是
初始状态 16471352 (几乎成功的初始状态,06471352 即为八皇后的一个解)
初始状态 45634565 (书本上的初始状态)
随机初始状态
观察到,对于
几乎成功的初始状态,最陡上升爬山法成功找到了解。
书本上的初始状态,最陡上升爬山法未能找到解,且和书上一样最后卡在了 h = 1 的状态。
随机初始状态,最陡上升爬山法未能找到解。
对于这三次测试,容易发现,h 值(也即相互攻击的皇后的对数)都下降了,也即最陡上升爬山法虽然不一定得到全局最大值,但确实改善了八皇后问题的状态,使其到达了一个较好的局部最大值。
void SHC_test2():最陡上升爬山法测试函数 —— 进行 1000 次最陡上升爬山法求解测试,统计最陡上升爬山法的成功几率,成功平均步数和失败平均步数
2.2 首选爬山法 2.2.1 代码实现
和最陡上升爬山法只有非常细微的差别。最陡上升爬山法中,我们需要对当前状态的所有后继状态进行尝试,然后选出其中评估值最优的后继状态作为我们的后继状态 ,这也即最陡上升 ;而在首选爬山法中,我们一旦找到一个比当前状态评估值更优的后继状态,我们就将其作为后继状态 ,这也即首选 。不难理解,首选爬山法的效率会比最陡上升爬山法低。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 bool First_Choice_Hill_Climbing (Board* board) int steps = 0 ; string old_state = board->get_state (); string new_state = old_state; string best_state = old_state; int min_h = board->h_of_attack_pair (); int new_h; while (1 ) { ++steps; bool find_flag = false ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 8 ; ++j) { if (old_state[i] != j + '0' ) { new_state = old_state; new_state[i] = j + '0' ; board->set_state (new_state); board->fill_in_board (); new_h = board->h_of_attack_pair (); board->h_value_board[j][i] = new_h; if (new_h < min_h) { min_h = new_h; best_state = new_state; find_flag = true ; if (min_h == 0 ) { FCHC_success_total_steps += steps; return true ; } break ; } } else board->h_value_board[j][i] = 0 ; } if (find_flag) break ; } board->set_state (best_state); board->fill_in_board (); if (!find_flag) { FCHC_failed_total_steps += steps; return false ; } old_state = best_state; } }
2.2.2 测试
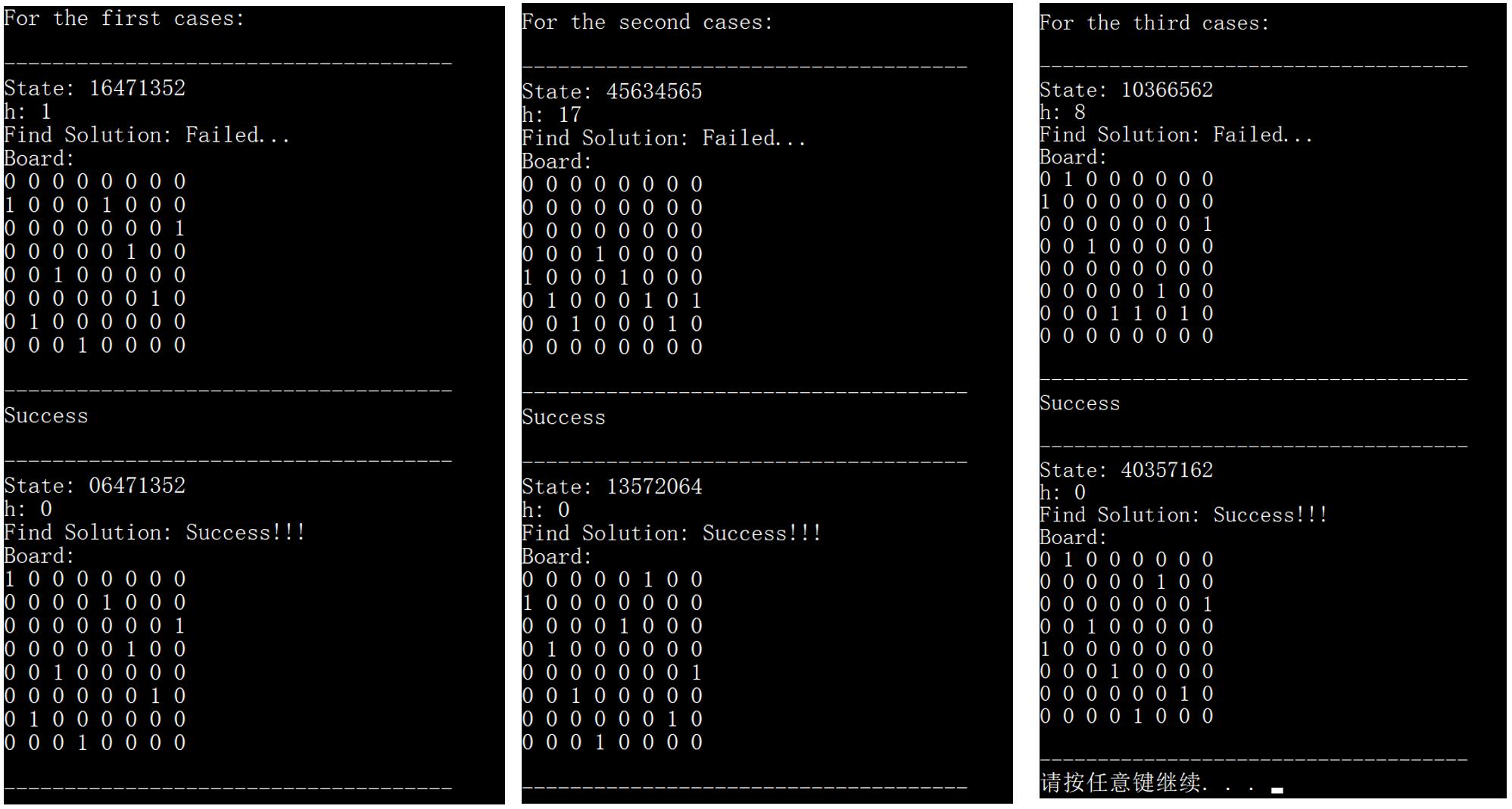
void FCHC_test1():首选爬山法测试函数 —— 进行 3 次首选爬山法求解测试,分别是
初始状态 16471352 (几乎成功的初始状态,06471352 即为八皇后的一个解)
初始状态 45634565 (书本上的初始状态)
随机初始状态
观察到,对于
几乎成功的初始状态,首选爬山法成功找到了解。
书本上的初始状态,首选爬山法未能找到解,和最陡上升爬山法不一样,首选爬山法最后卡在了 h = 2 的状态。
随机初始状态,首选爬山法未能找到解。
对于这三次测试,容易发现,h 值(也即相互攻击的皇后的对数)都下降了,也即首选爬山法虽然不一定得到全局最大值,但确实改善了八皇后问题的状态,使其到达了一个较好的局部最大值。
void SHC_test2():首选爬山法测试函数 —— 进行 1000 次首选爬山法求解测试,统计首选爬山法的成功几率,成功平均步数和失败平均步数
正如我们所预期的那样,首选爬山法和最陡上升爬山法的成功几率相近,但相较于最陡上升爬山法,首选爬山法的成功平均步数和失败平均步数都明显更大一些,这也即意味着首选爬山法的效率更低。
2.3 随机重启爬山法
我们选择最陡上升 作为随机重启爬山法的爬山策略,当最陡上升爬山法遇到局部最大值而失败,我们将随机生成一个新的初始状态再次使用最陡上升爬山法重启爬山。为简单探求随机重启爬山法的完备性,我们设置重启次数上限为 1000 次。
2.3.1 代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 bool Random_Restart_Steepest_Hill_Climbing (Board* board) for (int i = 0 ; i < 1000 ; ++i) { if (!Steepest_Hill_Climbing (board)) { board->random_initial_state (); board->fill_in_board (); } else { RRSHC_success_total_steps += (SHC_failed_total_steps + SHC_success_total_steps); SHC_success_total_steps = 0 ; SHC_failed_total_steps = 0 ; return true ; } } RRSHC_failed_total_steps += (SHC_failed_total_steps + SHC_success_total_steps); SHC_success_total_steps = 0 ; SHC_failed_total_steps = 0 ; return false ; }
2.3.2 测试
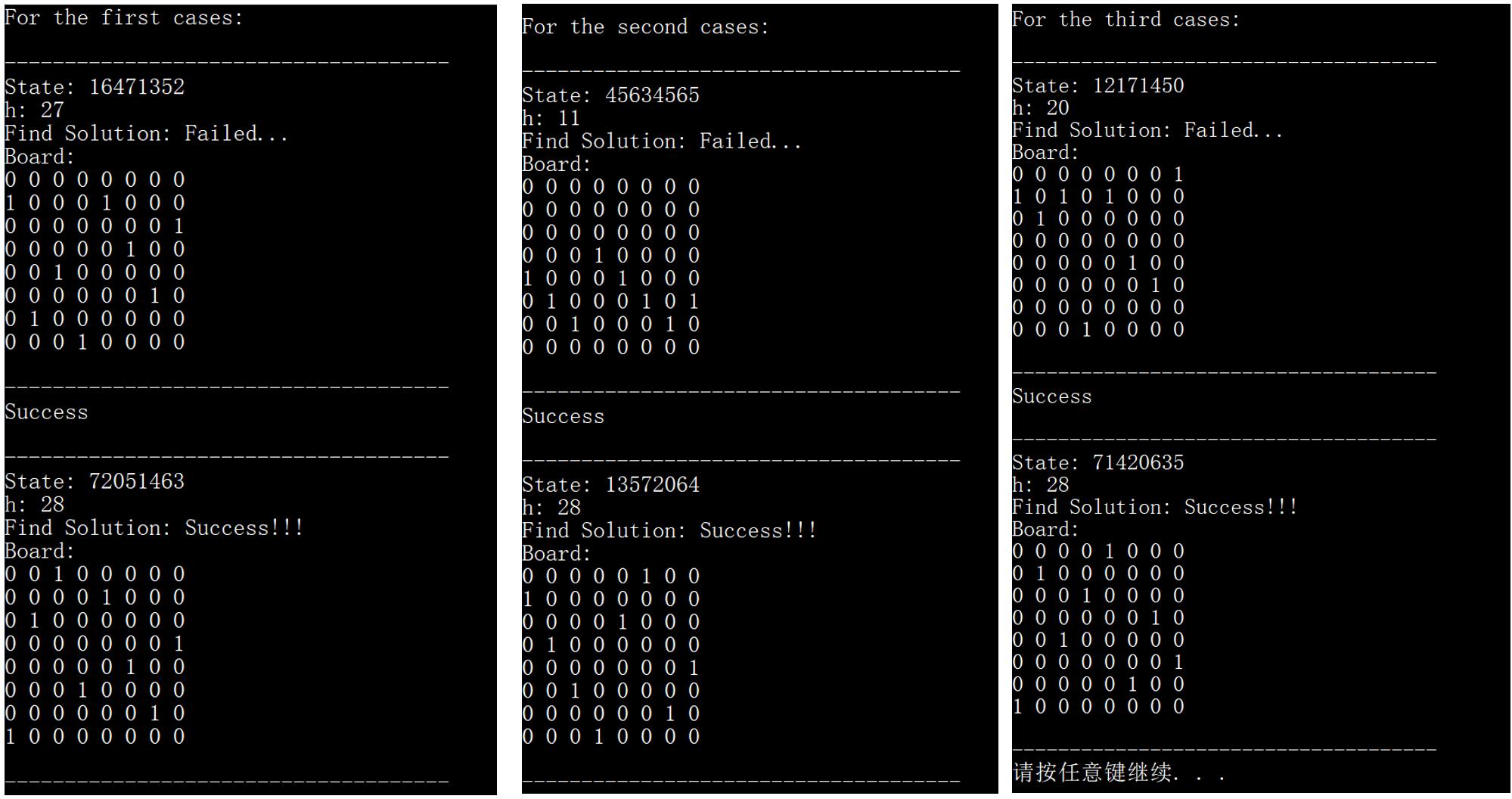
void RRSHC_test1():随机重启爬山法测试函数 —— 进行 3 次随机重启爬山法求解测试,分别是
初始状态 16471352 (几乎成功的初始状态,06471352 即为八皇后的一个解)
初始状态 45634565 (书本上的初始状态)
随机初始状态
观察到,对于三种初始状态,随机重启爬山法都成功找到了解 。
void RRSHC_test2():随机重启爬山法测试函数 —— 进行 1000 次随机重启爬山法求解测试,统计随机重启爬山法的成功几率,成功平均步数和失败平均步数
可以看到随机重启爬山法总是成功的 。正如书上所说的那样:随机重启爬山法完备的概率接近于 1 ,因为只要随机重启的次数上限足够大,那么最终我们能够随机重启生成一个目标状态(成功状态)作为初始状态。对于八皇后问题而言,随机重启次数上限为 1000 次已经基本能够保证找到解。
设置不同的随机重启次数上限,调用 RRSHC_test2() 以探究对于八皇后问题而言较好的随机重启上限
随机重启次数上限
成功求解概率
成功平均步数
失败平均步数
5
0.559
10.5331
20.4807
10
0.806
17.4169
40.6856
20
0.955
23.5403
82.4667
50
1
28.813
never failed
可以看到,对于八皇后问题而言,50次随机重启,算法已经是几乎完备的。
3. 模拟退火
相比于爬山法,模拟退火最大的特点是:允许下山 。如果温度下降得足够慢,也即退火足够慢,那么模拟退火算法找到全局最优解的概率逼近于 1。
我们先简要介绍并分析一下模拟退火算法。
对于八皇后问题而言,模拟退火算法随机抽取 1 个当前状态的后继状态 。既然是随机抽取,那么就必然存在随机抽取的新的后继状态会比当前状态要差的情况,在下面的代码中,我们使用不相互攻击的皇后的数量 h_of_not_attack_pair() 来计算状态的评估值 ,评估值被用作评判状态好坏的依据。
如果我们的新状态比当前状态要好,也即评估值更优,那么模拟退火算法会欣然接受这个新的状态。
如果我们的新状态比当前状态要差,也即评估值更差,那么模拟退火算法不会像爬山法一样丢弃这个新的状态,而是允许下山:模拟退火算法以某个小于 1 的概率接受这个新的状态 。
这个概率的设计,同样是模拟退火算法的关键 。
下面分析代码中使用的八皇后问题的概率公式:
因为我们使用不相互攻击的皇后的数量来计算状态的评估值,所以如果后继 next 的状态相对更差,那么其不相互攻击的皇后数量是更少的,这也即 $\Delta E < 0$ 。又因为 $T$ 总是个正数,所以 $\frac{\Delta E}{T} < 0$ ,结合 $y=e^x$ 图像可知,$P=e^\frac{\Delta E}{T}<1$,这说明代码中的模拟退火算法确实是以小于 1 的概率接受这个新的状态。
$P=e^\frac{\Delta E}{T}$ 中有两个变量,分别是 $\Delta E$ 和 $T$。
我们从一个短的时间段看待 $P$,则 $T$ 在短时间内几乎没有什么变化(设计上也是这样要求的 —— 退火越慢算法越完备),那么此时影响 $P$ 的主要变量是 $\Delta E$。 此时,如果后继状态相比于当前状态越差,那么 $\Delta E$ 就会越负(本身就已经小于 0),$P$ 就越小,较差的后继状态就越不可能被接受。
我们从一个长的时间段看待 $P$,则 $\Delta E$ 在长时间段上的变化是类似的,因为后继状态是随机挑选的,且 $\Delta E$ 变化再大,也是有上限的,对于当前的八皇后问题而言,$\Delta E$ 的变化不可能绝对值大于 28。换句话说,在长时间段上,影响 $P$ 的主要变量是 $T$。
一开始, $T$ 的值为 5(代码实现里初始温度设为 5),但经过较长的时间之后,$T$ 的值会变为 0.01,甚至更小。假设 $\Delta E$ 不变(更直观地,假设$\Delta E=-3$),那么 $P_b=e^\frac{\Delta E}{5}=0.5488$,$P_e=e^\frac{\Delta E}{0.001}=e^\frac{500\Delta E}{5}=(P_b)^{500}=5.148e-131$。可见,对于同样差了 3 个等级的后继状态($\Delta E$),最开始模拟退火算法有大约一半的概率接受,而当 $T$ 的值变的较小时,较差的后继状态几乎不可能被接受。
而这一点是模拟退火算法概率设计的关键:一开始,模拟退火算法接受较差后继状态的概率较大,越往后,模拟退火算法就越不可能接受一个较差的后继状态 。
书上也有个形象的例子:想象在高低不平的平面上有个乒乓球想掉落到最深的裂缝中去,那么模拟退火的方法就是一开始使劲摇晃(先高温加热)然后慢慢降低摇晃的强度(后逐渐降温)。
3.1 代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 float schedule (float T) return 0.99 * T; } bool Simulated_Annealing (Board* board, float (*p)(float )) int steps = 0 ; double T = 5 ; string old_state = board->get_state (); string new_state = old_state; int old_value = 0 ; int new_value = 0 ; while (T > 0.00001 ) { ++steps; old_value = board->h_of_not_attack_pair (); if (board->check (1 )) { SA_success_total_steps += steps; return true ; } T = (*p)(T); int y = rand () % 8 ; int x = 0 ; while (1 ) { x = rand () % 8 ; if (x != old_state[y] - '0' ) break ; } new_state = old_state; new_state[y] = x + '0' ; board->set_state (new_state); board->fill_in_board (); new_value = board->h_of_not_attack_pair (); int deltaE = (new_value - old_value); if (deltaE > 0 ) { old_state = new_state; } else { if (((float )(rand () % 1000 ) / 1000 ) < exp (deltaE / T)) { old_state = new_state; } else { board->set_state (old_state); board->fill_in_board (); } } } SA_failed_total_steps += steps; return false ; }
3.2 测试
void SA_test1():模拟退火测试函数 —— 进行 3 次模拟退火求解测试,分别是
初始状态 16471352 (几乎成功的初始状态,06471352 即为八皇后的一个解)
初始状态 45634565 (书本上的初始状态)
随机初始状态
观察到,对于三种初始状态,模拟退火都成功找到了解 。注意,在爬山法里解的 h 值为 0,但在模拟退火里解的 h 值为 28,这是因为前者使用相互攻击的皇后的对数作为启发式评估函数,后者使用不相互攻击的皇后的对数作为启发式评估函数。
void SA_test2():模拟退火测试函数 —— 进行 1000 次模拟退火求解测试,统计模拟退火的成功几率,成功平均步数和失败平均步数
虽然在 SA_test1() 中三次都成功都找到了解,但实际上对于初始温度 $T=5$,退火函数 $T = 0.99 T$ 的模拟退火,我们并不总能成功找到解 ,成功的概率是 0.781。而相比爬山法,容易发现模拟退火的成功平均步数和失败平均步数都发生了巨大的递增。这反映了爬山法确实效率很高,这是优点也是缺点。
设置不同的退火速率,调用 SA_test2() 以探究退火速率对于八皇后问题求解的完备性的影响 :
退火速率
成功求解概率
成功平均步数
失败平均步数
T=0.99T
0.781
593.36
1311.96
T=0.999T
0.998
2578.48
13116
T=0.9999T
1
13465.4
never failed
退火越缓慢,模拟退火成功求解八皇后问题的概率就越高,但随着成功求解概率的提高,成功平均步数和失败平均步数也明显提高。
4. 遗传算法
遗传算法是随机束搜索的一个变形,其最关键的思想在于模拟自然选择,有性繁殖以及模式理论。
遗传算法实际上用书本上一幅图基本上就能概括:
像束搜索一样,最开始我们具有若干个随机生成的初始状态,这些初始状态被称为种群 ,也即图中 a 的初始种群。
类比自然选择,遗传算法中,我们确保种群中较好的状态有较大概率参与下一代的繁殖,而较差的状态能够繁殖自己后代的概率较小,我们使用适应度函数来评价种群中的状态 ,而在这里我们使用不相互攻击的皇后的对数 h_of_not_attack_pair() 作为适应度函数,这对应着图中的 b 和 c 过程。
类比有性繁殖,我们将要配对的个体,在字符串中随机选择一个杂交点,配对的个体所产生的后代其杂交点前后的状态信息(基因)分别来自于两个参与配对的个体。
这里杂交的可行性来自于模式的思想的支持,如果状态信息(基因)的位置在初始的时候就允许随机转换,那么杂交就没有优势了,因为直观上说,杂交有助于将独立发展出来的有利模式结合起来,提高了搜索的粒度 。
对于整个种群,适应较强的个体其状态信息的一部分也是较优的,也即模式是较优的。较优的模式进行组合,那么我们更容易得到一个整体最优的后代。
最后,我们还模拟了遗传过程中可能发生的变异,这一点同样是遗传算法成功的关键。
4.1 代码实现 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 string Random_Selection (vector<string> &p) { int total_value = 0 ; vector<int > h (p.size()) ; vector<int > rand_array; for (int i = 0 ; i < p.size (); ++i) { b_tool.set_state (p[i]); b_tool.fill_in_board (); h[i] = b_tool.h_of_not_attack_pair (); total_value += h[i]; } for (int i = 0 ; i < p.size (); ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < h[i]; ++j) { rand_array.push_back (i); } } int rv = rand () % total_value; return p[rand_array[rv]]; } string Reproduce (string x, string y) { int cut = rand () % 7 ; cut++; return x.substr (0 , cut) + y.substr (cut); } bool Mutate (string &s, float rate) int rand_mutate_pos = rand () % 64 ; string new_s = s; int h = 0 ; int new_h = 0 ; if (((float )(rand () % 1000 ) / 1000 ) < rate) { new_s[rand_mutate_pos / 8 ] = (rand_mutate_pos % 8 ) + '0' ; b_tool.set_state (new_s); b_tool.fill_in_board (); new_h = b_tool.h_of_not_attack_pair (); b_tool.set_state (s); b_tool.fill_in_board (); h = b_tool.h_of_not_attack_pair (); if (new_h >= h) s = new_s; return true ; } return false ; } void print_p (const vector<string>& p) cout << endl; for (auto str : p) { b_tool.set_state (str); b_tool.fill_in_board (); cout << str << " : " << b_tool.h_of_not_attack_pair () << endl; } cout << endl; } bool Genetic_Algorithn (vector<string> &p, float mutate_rate) vector<string> old_p = p; vector<string> new_p (p.size()) ; for (int n = 0 ; n < 10000 ; ++n) { for (int i = 0 ; i < p.size (); ++i) { string x = Random_Selection (old_p); string y = Random_Selection (old_p); string child = Reproduce (x, y); Mutate (child, mutate_rate); new_p[i] = child; b_tool.set_state (child); b_tool.fill_in_board (); if (b_tool.check (1 )) { p[0 ] = child; generation += n; return true ; } } old_p = new_p; print_p (old_p); } p = old_p; return false ; }
4.2 测试
void GA_test1(int p_size = 4, float mutate_rate = 0.5):遗传算法测试函数,默认情况下,设定遗传算法种群大小为 4 (按书本),变异概率为 0.5。
随机产生的初始种群为下图中红框圈住部分,记为第 0 代。后续为输出为 第 1 代,第 2 代以及第 3 代的种群情况。
第 15 代到第 18 代的种群情况:
遗传的代数越多,种群中的个体就越相似,这是无法避免的。 所以,此时变异的重要性就凸显出来了。如果没有变异,那么相似的个体进行杂交,其后代的状态信息(基因)将很可能和父母相同,进化就此停滞。而变异的普遍存在,确保了会有或者更优或者更差的不同后代的产生,而更优的后代往往更容易获得交配权,将其优秀的状态信息扩散到种群中去,使得整个种群发生进化。
最终,遗传算法在第 289 代找到了最完美的后代,其即为八皇后问题的解:
void GA_test2(int p_size = 4, float mutate_rate = 0.5):遗传算法测试函数 —— 进行 1000 次遗传算法求解测试,统计遗传算法的成功几率,成功平均代数,失败平均代数不需要统计(即为设定的 10000 代)
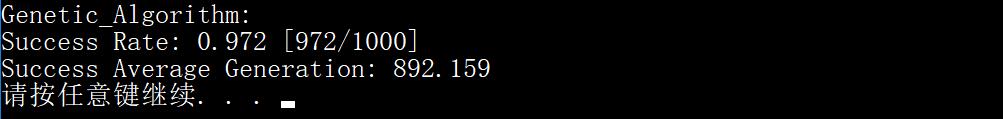
遗传算法的成功求解概率为 0.972,成功平均代数为 892.159,由于运行 GA_test2() 时使用默认的种群大小 4,所以容易求得遗传算法的成功平均步数为 4 $\times$ 892.159 = 3568.636,比模拟退火中 $T=0.999T\times$ 的成功平均步长还要更长一点,但 GA_test2() 运行起来明显花费了更长的时间,我猜想这应该是因为遗传算法的失败代价过高
除了以上的测试,还可以设置不同的种群大小和变异概率,调用 GA_test2() 以探究不同的种群大小和变异概率对于八皇后问题求解成功概率和成功平均代数的影响。但鉴于跑一次 GA_test2() 时间过长,所以在这里没有具体进行尝试 。
4.3 实现过程中遇到的问题与思考 主要的问题还是遗传算法效率过低 。
遗传算法很容易进入种群内所有个体都基本一样的情境,一旦进入这种情境,遗传算法的种群进化进程将立刻大大减缓。
在种群内个体状态信息(基因型)很多样的时候,杂交能够进一步促进基因的多样性,此外还能变异也能产生新的基因型,所以种群内的总是能够涌现出当前种群中没有的新基因型,一旦新的基因型适应能力更强,那么新的基因型将很容易在种群中传播开。
一旦种群内个体状态信息(基因型)大部分都相似的时候,往往杂交所得后代基因型也与父母的基因型没有太大差别,此时种群要产生新的基因型只能依靠变异,而变异又应该是小概率的,这就使得种群的进化几乎停滞了。
如果只是最基本地实现书上所提到的变异函数,那么基本上大小为 4 的种群在 10000 代内,遗传算法也很大可能不可以找到解。
因此,我的代码实现中的 Mutate(string &s, float rate) 函数不得不对书上所提到的变异函数做了很多额外的改动:设置了较高的变异概率且只保留适应度函数评价大于等于当前状态的变异,这大概借鉴了一点胚胎致死的思想(如果变异不比当前状态好,那么生出来的机会都没有)。这些改动有助于加快种群的进化。
仔细思考,遗传算法很容易进入所有个体都基本一样的情境实际上也和基因过于简单有关。而现实生活中变异发生的概率虽然低,但是因为基因数量很大,所以在父母和后代之间,基因型几乎比如发生了变化,所以在八皇后实验中,设置较高的变异概率也可视为一种对现实环境的更贴切的模拟,而这也确实提高了遗传算法的效率。
5. 完整代码 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525 526 527 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 544 545 546 547 548 549 550 551 552 553 554 555 556 557 558 559 560 561 562 563 564 565 566 567 568 569 570 571 572 573 574 575 576 577 578 579 580 581 582 583 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 613 614 615 616 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 645 646 647 648 649 650 651 652 653 654 655 656 657 658 659 660 661 662 663 664 665 666 667 668 669 670 671 672 673 674 675 676 677 678 679 680 681 682 683 684 685 686 687 688 689 690 691 692 693 694 695 696 697 698 699 700 701 702 703 704 705 706 707 708 709 710 711 712 713 714 715 716 717 718 719 720 721 722 723 724 725 726 727 728 729 730 731 732 733 734 735 736 737 738 739 740 741 742 743 744 745 746 747 748 749 750 751 752 #include <iostream> #include <ctime> #include <string> #include <cmath> #include <vector> using namespace ::std;int SHC_success_total_steps = 0 ; int SHC_failed_total_steps = 0 ; int FCHC_success_total_steps = 0 ; int FCHC_failed_total_steps = 0 ; int RRSHC_success_total_steps = 0 ; int RRSHC_failed_total_steps = 0 ; int SA_success_total_steps = 0 ; int SA_failed_total_steps = 0 ; int generation = 0 ; class Board {public : void fill_in_board () initial (); for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { board[state[i]][i] = true ; } } void initial () for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 8 ; ++j) { board[i][j] = false ; } } } void random_initial_state () for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { state[i] = rand () % 8 ; } } void display (int mode) cout << endl << "-------------------------------------" << endl; cout << "State: " << get_state () << endl << "h: " << (mode == 0 ? h_of_attack_pair () : h_of_not_attack_pair ()) << endl << "Find Solution: " << (check (mode) ? "Success!!!" : "Failed..." ) << endl << "Board: " << endl; for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 8 ; ++j) { cout << board[i][j] << " " ; } cout << endl; } cout << endl << "-------------------------------------" << endl; } void display_h_value_on_board () cout << "H_Value On Board: " << endl; for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 8 ; ++j) { cout << h_value_board[i][j] << " " ; } cout << endl; } } void set_state (string state_) for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { state[i] = state_[i] - '0' ; } } string get_state () { string res; for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { res += state[i] + '0' ; } return res; } bool check (int mode) if (mode == 0 ) return h_of_attack_pair () == 0 ; else return h_of_not_attack_pair () == 28 ; } int h_of_attack_pair () int value = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { value += count_attack (state[i], i); } return value / 2 ; } int h_of_not_attack_pair () int value = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { value += (7 - count_attack (state[i], i)); } return value / 2 ; } int count_attack (int x, int y) int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { if (i != y && board[x][i]) { count++; } } for (int i = x, j = y; i > 0 && j > 0 ; ) { if (board[--i][--j]) count++; } for (int i = x, j = y; i < 7 && j < 7 ; ) { if (board[++i][++j]) count++; } for (int i = x, j = y; i > 0 && j < 7 ; ) { if (board[--i][++j]) count++; } for (int i = x, j = y; i < 7 && j > 0 ; ) { if (board[++i][--j]) count++; } return count; } int h_value_board[8 ][8 ] = {}; private : bool board[8 ][8 ]; int state[8 ]; }; Board b_tool; bool Steepest_Hill_Climbing (Board* board) int steps = 0 ; string old_state = board->get_state (); string new_state = old_state; string best_state = old_state; int min_h = board->h_of_attack_pair (); int new_h; while (1 ) { ++steps; bool local_max_flag = true ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 8 ; ++j) { if (old_state[i] != j + '0' ) { new_state = old_state; new_state[i] = j + '0' ; board->set_state (new_state); board->fill_in_board (); new_h = board->h_of_attack_pair (); board->h_value_board[j][i] = new_h; if (new_h < min_h) { min_h = new_h; best_state = new_state; local_max_flag = false ; if (min_h == 0 ) { SHC_success_total_steps += steps; return true ; } } } else board->h_value_board[j][i] = 0 ; } } board->set_state (best_state); board->fill_in_board (); if (local_max_flag) { SHC_failed_total_steps += steps; return false ; } old_state = best_state; } } bool First_Choice_Hill_Climbing (Board* board) int steps = 0 ; string old_state = board->get_state (); string new_state = old_state; string best_state = old_state; int min_h = board->h_of_attack_pair (); int new_h; while (1 ) { ++steps; bool find_flag = false ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 8 ; ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < 8 ; ++j) { if (old_state[i] != j + '0' ) { new_state = old_state; new_state[i] = j + '0' ; board->set_state (new_state); board->fill_in_board (); new_h = board->h_of_attack_pair (); board->h_value_board[j][i] = new_h; if (new_h < min_h) { min_h = new_h; best_state = new_state; find_flag = true ; if (min_h == 0 ) { FCHC_success_total_steps += steps; return true ; } break ; } } else board->h_value_board[j][i] = 0 ; } if (find_flag) break ; } board->set_state (best_state); board->fill_in_board (); if (!find_flag) { FCHC_failed_total_steps += steps; return false ; } old_state = best_state; } } bool Random_Restart_Steepest_Hill_Climbing (Board* board) for (int i = 0 ; i < 50 ; ++i) { if (!Steepest_Hill_Climbing (board)) { board->random_initial_state (); board->fill_in_board (); } else { RRSHC_success_total_steps += (SHC_failed_total_steps + SHC_success_total_steps); SHC_success_total_steps = 0 ; SHC_failed_total_steps = 0 ; return true ; } } RRSHC_failed_total_steps += (SHC_failed_total_steps + SHC_success_total_steps); SHC_success_total_steps = 0 ; SHC_failed_total_steps = 0 ; return false ; } void SHC_test1 () Board board; cout << "For the first cases: " << endl; board.initial (); board.set_state ("16471352" ); board.fill_in_board (); board.display (0 ); Steepest_Hill_Climbing (&board); if (board.check (0 )) { cout << "Success" << endl; } else cout << "Failed" << endl; board.display (0 ); cout << endl; cout << "For the second cases: " << endl; board.set_state ("45634565" ); board.fill_in_board (); board.display (0 ); Steepest_Hill_Climbing (&board); if (board.check (0 )) { cout << "Success" << endl; } else cout << "Failed" << endl; board.display (0 ); cout << endl; cout << "For the third cases: " << endl; board.random_initial_state (); board.fill_in_board (); board.display (0 ); Steepest_Hill_Climbing (&board); if (board.check (0 )) { cout << "Success" << endl; } else cout << "Failed" << endl; board.display (0 ); } void SHC_test2 () Board board; int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 1000 ; ++i) { board.initial (); board.random_initial_state (); board.fill_in_board (); cout << board.get_state () << endl; Steepest_Hill_Climbing (&board); if (board.check (0 )) { ++count; } } cout << "Steepest_Hill_Climbing: " << endl << "Success Rate: " << float (count) / 1000 << " [" << count << "/1000]" << endl << "Success average steps: " << float (SHC_success_total_steps) / count << endl << "Failed average steps: " << float (SHC_failed_total_steps) / (1000 - count) << endl; } void FCHC_test1 () Board board; cout << "For the first cases: " << endl; board.initial (); board.set_state ("16471352" ); board.fill_in_board (); board.display (0 ); First_Choice_Hill_Climbing (&board); if (board.check (0 )) { cout << "Success" << endl; } else cout << "Failed" << endl; board.display (0 ); cout << endl; cout << "For the second cases: " << endl; board.set_state ("45634565" ); board.fill_in_board (); board.display (0 ); First_Choice_Hill_Climbing (&board); if (board.check (0 )) { cout << "Success" << endl; } else cout << "Failed" << endl; board.display (0 ); cout << endl; cout << "For the third cases: " << endl; board.random_initial_state (); board.fill_in_board (); board.display (0 ); First_Choice_Hill_Climbing (&board); if (board.check (0 )) { cout << "Success" << endl; } else cout << "Failed" << endl; board.display (0 ); } void FCHC_test2 () Board board; int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 1000 ; ++i) { board.initial (); board.random_initial_state (); board.fill_in_board (); cout << board.get_state () << endl; First_Choice_Hill_Climbing (&board); if (board.check (0 )) ++count; } cout << "First_Choice_Hill_Climbing: " << endl << "Success Rate: " << float (count) / 1000 << " [" << count << "/1000]" << endl << "Success average steps: " << float (FCHC_success_total_steps) / count << endl << "Failed average steps: " << float (FCHC_failed_total_steps) / (1000 - count) << endl; } void RRSHC_test1 () Board board; cout << "For the first cases: " << endl; board.initial (); board.set_state ("16471352" ); board.fill_in_board (); board.display (0 ); Random_Restart_Steepest_Hill_Climbing (&board); if (board.check (0 )) { cout << "Success" << endl; } else cout << "Failed" << endl; board.display (0 ); cout << endl; cout << "For the second cases: " << endl; board.set_state ("45634565" ); board.fill_in_board (); board.display (0 ); Random_Restart_Steepest_Hill_Climbing (&board); if (board.check (0 )) { cout << "Success" << endl; } else cout << "Failed" << endl; board.display (0 ); cout << endl; cout << "For the third cases: " << endl; board.random_initial_state (); board.fill_in_board (); board.display (0 ); Random_Restart_Steepest_Hill_Climbing (&board); if (board.check (0 )) { cout << "Success" << endl; } else cout << "Failed" << endl; board.display (0 ); } void RRSHC_test2 () Board board; int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 1000 ; ++i) { board.initial (); board.random_initial_state (); board.fill_in_board (); cout << board.get_state () << endl; Random_Restart_Steepest_Hill_Climbing (&board); if (board.check (0 )) ++count; } cout << "Random_Start_Steepest_Hill_Climbing: " << endl << "Success Rate: " << float (count) / 1000 << " [" << count << "/1000]" << endl << "Success average steps: " << float (RRSHC_success_total_steps) / count << endl; cout << "Failed average steps: " ; if (1000 - count == 0 ) cout << "never failed" << endl; else cout << float (RRSHC_failed_total_steps) / (1000 - count) << endl; } float schedule (float T) return 0.9999 * T; } bool Simulated_Annealing (Board* board, float (*p)(float )) int steps = 0 ; double T = 5 ; string old_state = board->get_state (); string new_state = old_state; int old_value = 0 ; int new_value = 0 ; while (T > 0.00001 ) { ++steps; old_value = board->h_of_not_attack_pair (); if (board->check (1 )) { SA_success_total_steps += steps; return true ; } T = (*p)(T); int y = rand () % 8 ; int x = 0 ; while (1 ) { x = rand () % 8 ; if (x != old_state[y] - '0' ) break ; } new_state = old_state; new_state[y] = x + '0' ; board->set_state (new_state); board->fill_in_board (); new_value = board->h_of_not_attack_pair (); int deltaE = (new_value - old_value); if (deltaE > 0 ) { old_state = new_state; } else { if (((float )(rand () % 1000 ) / 1000 ) < exp (deltaE / T)) { old_state = new_state; } else { board->set_state (old_state); board->fill_in_board (); } } } SA_failed_total_steps += steps; return false ; } void SA_test1 () Board board; cout << "For the first cases: " << endl; board.initial (); board.set_state ("16471352" ); board.fill_in_board (); board.display (1 ); Simulated_Annealing (&board, &schedule); if (board.check (1 )) { cout << "Success" << endl; } else cout << "Failed" << endl; board.display (1 ); cout << endl; cout << "For the second cases: " << endl; board.set_state ("45634565" ); board.fill_in_board (); board.display (1 ); Simulated_Annealing (&board, &schedule); if (board.check (1 )) { cout << "Success" << endl; } else cout << "Failed" << endl; board.display (1 ); cout << endl; cout << "For the third cases: " << endl; board.random_initial_state (); board.fill_in_board (); board.display (1 ); Simulated_Annealing (&board, &schedule); if (board.check (1 )) { cout << "Success" << endl; } else cout << "Failed" << endl; board.display (1 ); } void SA_test2 () Board board; int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 1000 ; ++i) { board.initial (); board.random_initial_state (); board.fill_in_board (); cout << i << " : " << board.get_state () << endl; Simulated_Annealing (&board, schedule); if (board.check (1 )) ++count; } cout << "Simulated_Annealing_Hill_Climbing: " << endl << "Success Rate: " << float (count) / 1000 << " [" << count << "/1000]" << endl << "Success average steps: " << float (SA_success_total_steps) / count << endl; cout << "Failed average steps: " ; if (1000 - count == 0 ) cout << "never failed" << endl; else cout << float (SA_failed_total_steps) / (1000 - count) << endl; } string Random_Selection (vector<string> &p) { int total_value = 0 ; vector<int > h (p.size()) ; vector<int > rand_array; for (int i = 0 ; i < p.size (); ++i) { b_tool.set_state (p[i]); b_tool.fill_in_board (); h[i] = b_tool.h_of_not_attack_pair (); total_value += h[i]; } for (int i = 0 ; i < p.size (); ++i) { for (int j = 0 ; j < h[i]; ++j) { rand_array.push_back (i); } } int rv = rand () % total_value; return p[rand_array[rv]]; } string Reproduce (string x, string y) { int cut = rand () % 5 ; cut += 2 ; return x.substr (0 , cut) + y.substr (cut); } bool Mutate (string &s, float rate) int rand_mutate_pos = rand () % 64 ; string new_s = s; int h = 0 ; int new_h = 0 ; if (((float )(rand () % 1000 ) / 1000 ) < rate) { new_s[rand_mutate_pos / 8 ] = (rand_mutate_pos % 8 ) + '0' ; b_tool.set_state (new_s); b_tool.fill_in_board (); new_h = b_tool.h_of_not_attack_pair (); b_tool.set_state (s); b_tool.fill_in_board (); h = b_tool.h_of_not_attack_pair (); if (new_h >= h) s = new_s; return true ; } return false ; } void print_p (const vector<string>& p) for (auto str : p) { b_tool.set_state (str); b_tool.fill_in_board (); cout << str << " : " << b_tool.h_of_not_attack_pair () << endl; } cout << endl; } bool Genetic_Algorithn (vector<string> &p, float mutate_rate) vector<string> old_p = p; vector<string> new_p (p.size()) ; for (int n = 0 ; n < 1000 ; ++n) { for (int i = 0 ; i < p.size (); ++i) { string x = Random_Selection (old_p); string y = Random_Selection (old_p); string child = Reproduce (x, y); Mutate (child, mutate_rate); new_p[i] = child; b_tool.set_state (child); b_tool.fill_in_board (); if (b_tool.check (1 )) { p[0 ] = child; generation += n; return true ; } } old_p = new_p; } p = old_p; return false ; } bool GA_test1 (int p_size = 4 , float mutate_rate = 0.5 ) vector<string> p (p_size) ; for (int i = 0 ; i < p_size; ++i) { b_tool.random_initial_state (); b_tool.fill_in_board (); p[i] = b_tool.get_state (); cout << p[i] << " : " << b_tool.h_of_not_attack_pair () << endl; } if (Genetic_Algorithn (p, mutate_rate)) { b_tool.set_state (p[0 ]); b_tool.fill_in_board (); b_tool.display (1 ); return true ; } else { return false ; } } void GA_test2 (int p_size = 4 , float mutate_rate = 0.5 ) int count = 0 ; for (int i = 0 ; i < 1000 ; ++i) { cout << i << endl; if (GA_test1 (p_size, mutate_rate)) ++count; } cout << "Genetic_Algorithm: " << endl << "Success Rate: " << float (count) / 1000 << " [" << count << "/1000]" << endl << "Success Average Generation: " << float (generation) / count << endl; } int main () srand (time (0 )); return 0 ; }